EC2 Instance with Old AMI Remediation Guide
Overview
This tutorial demonstrates how to identify and remediate EC2 instances running on outdated AMIs (>365 days old). Using old AMIs poses security risks because they likely contain unpatched vulnerabilities and outdated software packages.
Prerequisites
- Access to AWS Console with EC2 permissions
- Instance ID flagged by the policy (example:
i-000e80a097e6006ea)
Step 1: Navigate to EC2 Instances Console
Navigate to the EC2 Instances console to locate the instance running on an outdated AMI.
URL: https://us-east-1.console.aws.amazon.com/ec2/home?region=us-east-1#Instances:
Step 2: Locate the Target Instance
In the search bar, enter the instance ID i-000e80a097e6006ea to filter for the specific instance flagged by the policy.
Step 3: Select the Instance
Click on the instance to view its details. The bottom panel shows instance metadata including the AMI ID used to launch this instance.
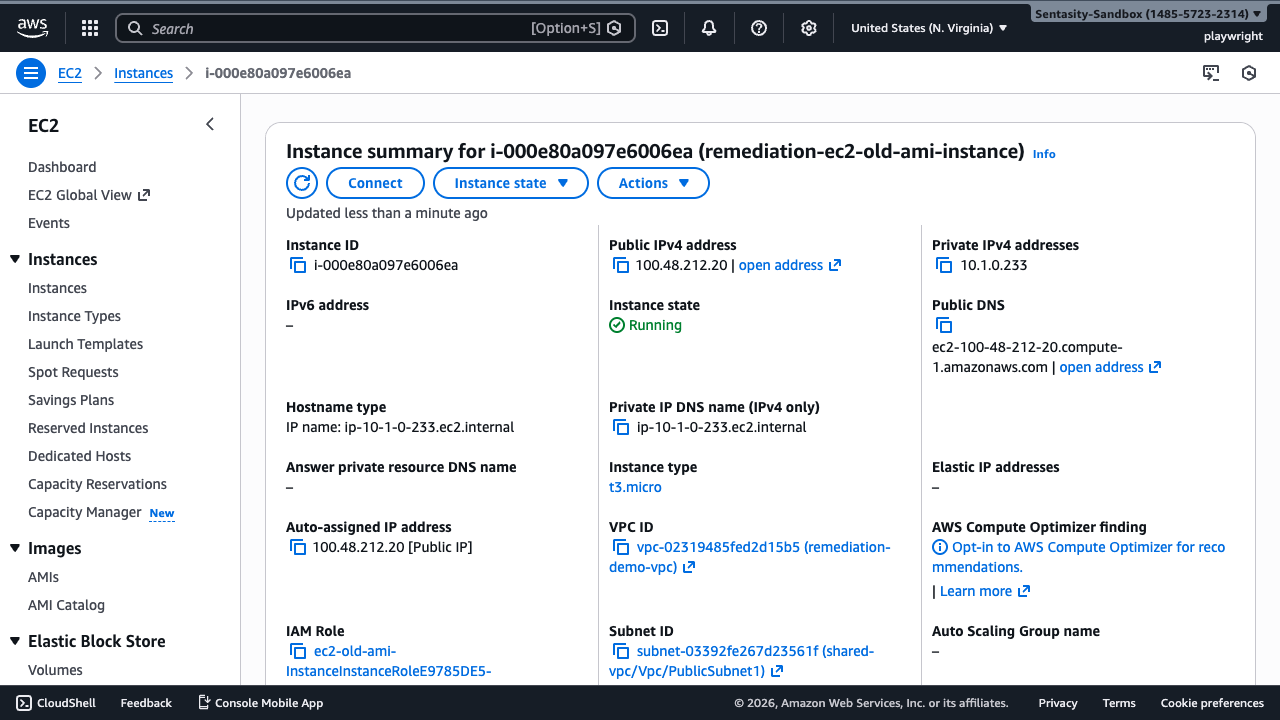
Step 4: Note the AMI ID
In the instance details panel, locate the AMI ID field. Note this value - you'll need it to verify the AMI's age and creation date.
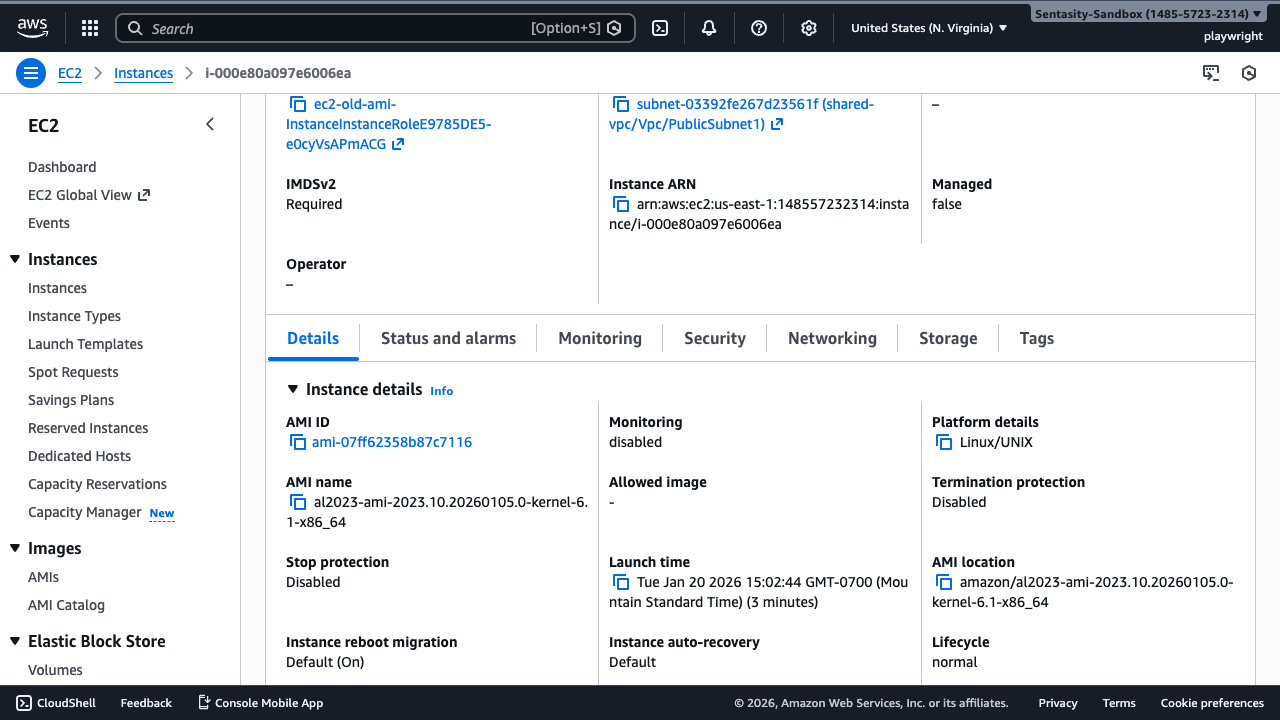
Step 5: Navigate to AMI Details
Click the AMI ID link to navigate to the AMI details page where you can verify its creation date.
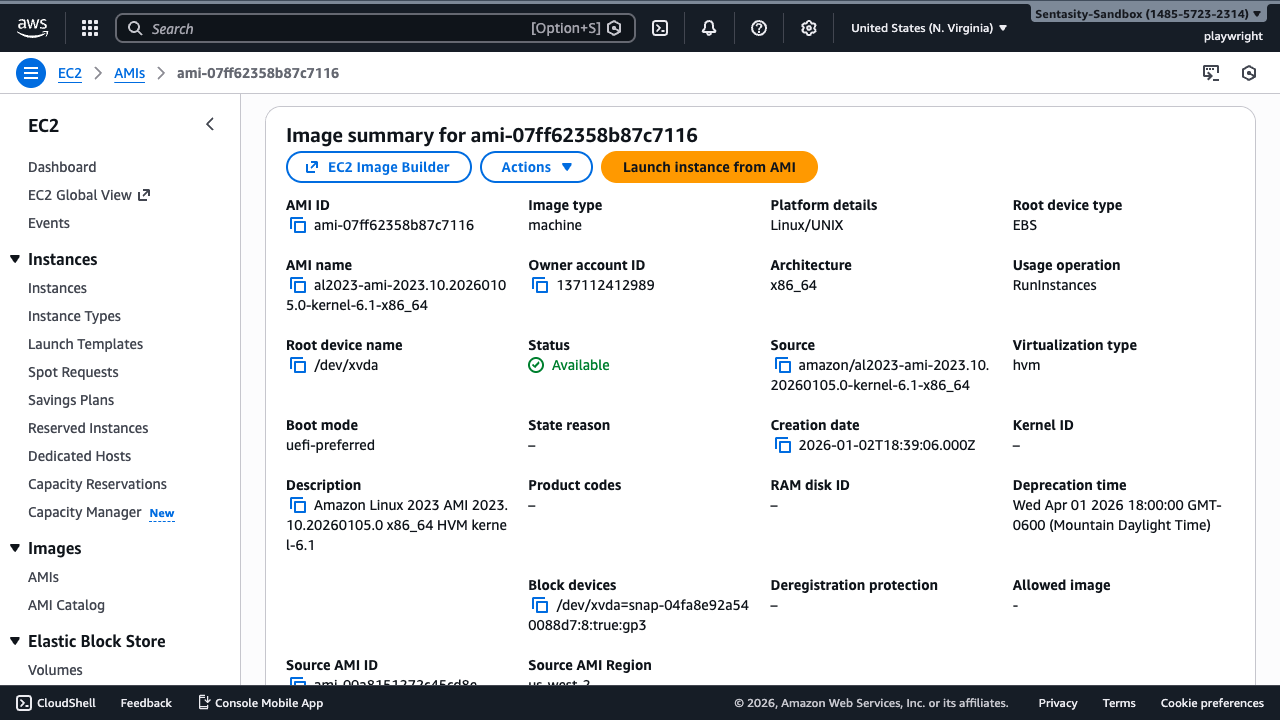
Step 6: Verify AMI Age
Check the Creation date field. If the AMI is older than 365 days, it likely contains unpatched vulnerabilities and outdated software packages that should be addressed.
Step 7: Return to Instance Details
Return to the instance details to plan your remediation approach.
Step 8: Plan Remediation Strategy
Remediation Options
Option 1: Replace with New AMI (Recommended)
- Create or identify an updated base AMI with current patches
- Launch new instance from updated AMI
- Migrate application data and configuration
- Update DNS/load balancer entries
- Terminate old instance
Option 2: In-Place Patching
- Use AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager
- Apply all available security updates
- Reboot instance to apply kernel patches
- Note: This doesn't update the base AMI age
Option 3: Rebuild with Image Builder
- Set up EC2 Image Builder pipeline
- Automate AMI refresh on a schedule
- Replace instances quarterly or monthly
Step 9: Document Risk Acceptance (If Deferring)
If you must defer remediation, add tags to document the risk acceptance and schedule replacement. Consider:
RiskAccepted=trueRemediationDueDate=YYYY-MM-DDJustification=legacy-app-pending-decomm
Cost Impact
No direct cost savings. This is a security remediation to reduce risk of breach due to unpatched vulnerabilities. Replacement involves standard EC2 compute costs. Delaying remediation increases security incident risk, which can far exceed infrastructure costs.
Alternative Approaches
- AWS Systems Manager Patch Manager: For ongoing patch compliance without full AMI replacement
- EC2 Image Builder: Automate golden AMI creation with scheduled rebuilds
- Immutable Infrastructure: Deploy new instances from fresh AMIs regularly, treat instances as disposable
- Compensating Controls: Network isolation, WAF rules, IDS/IPS if replacement isn't immediately feasible