How to Upgrade an EC2 Instance from Old Generation to Modern Type
This tutorial demonstrates how to upgrade an EC2 instance from an older generation instance type (t2.micro) to a modern equivalent (t3.micro), achieving approximately 10% cost savings with equal or better performance.
Cost Impact
Upgrading from t2.micro to t3.micro provides approximately 10% cost savings:
- t2.micro:
$8.47/month ($0.0116/hour) - t3.micro:
$7.59/month ($0.0104/hour) - Savings: ~$0.88/month per instance
For larger instance types (e.g., t2.large → t3.large), savings can reach $7-10/month per instance.
Prerequisites
- An EC2 instance running on an older generation instance type (e.g., t2.micro)
- AWS Console access with permissions to stop/start instances and modify instance types
- The instance must be in a stopped state to change its type
Step 1: Navigate to EC2 Instances
Navigate to the EC2 Instances console to view your running instances.
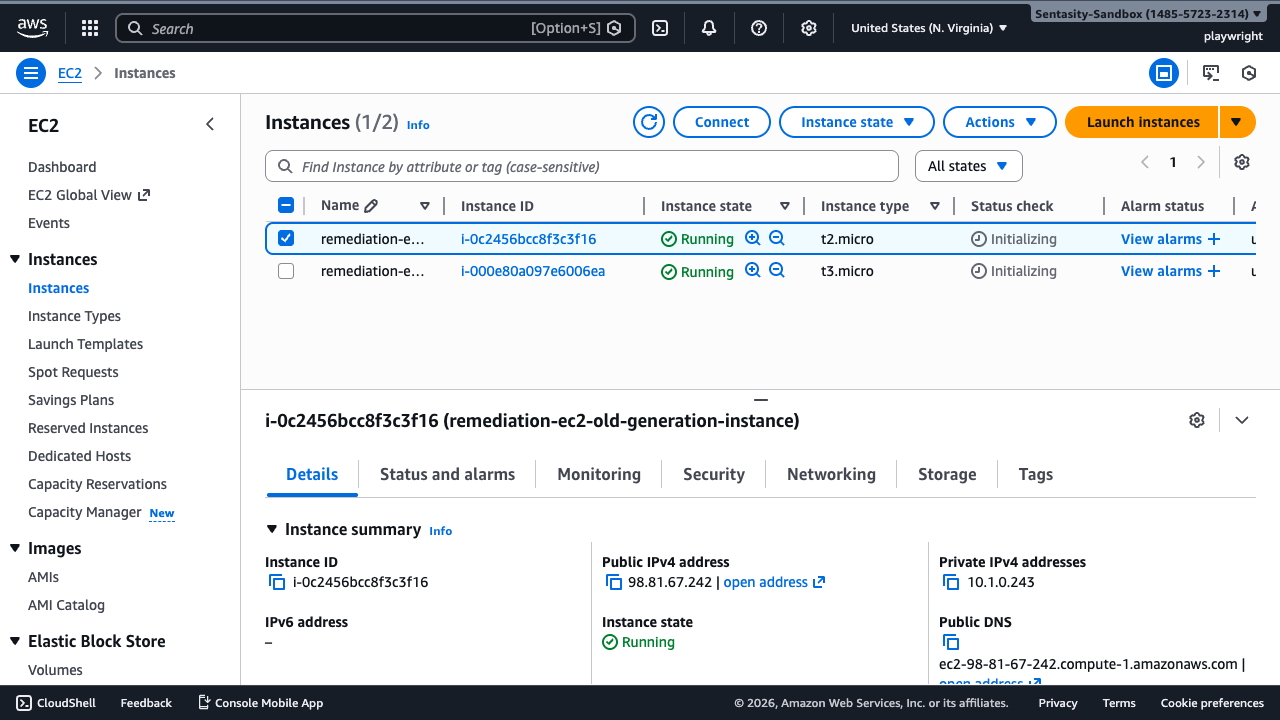
Step 2: Select the Target Instance
Select the instance you want to upgrade by clicking its checkbox. In this example, we're upgrading instance i-0c2456bcc8f3c3f16 running on t2.micro.
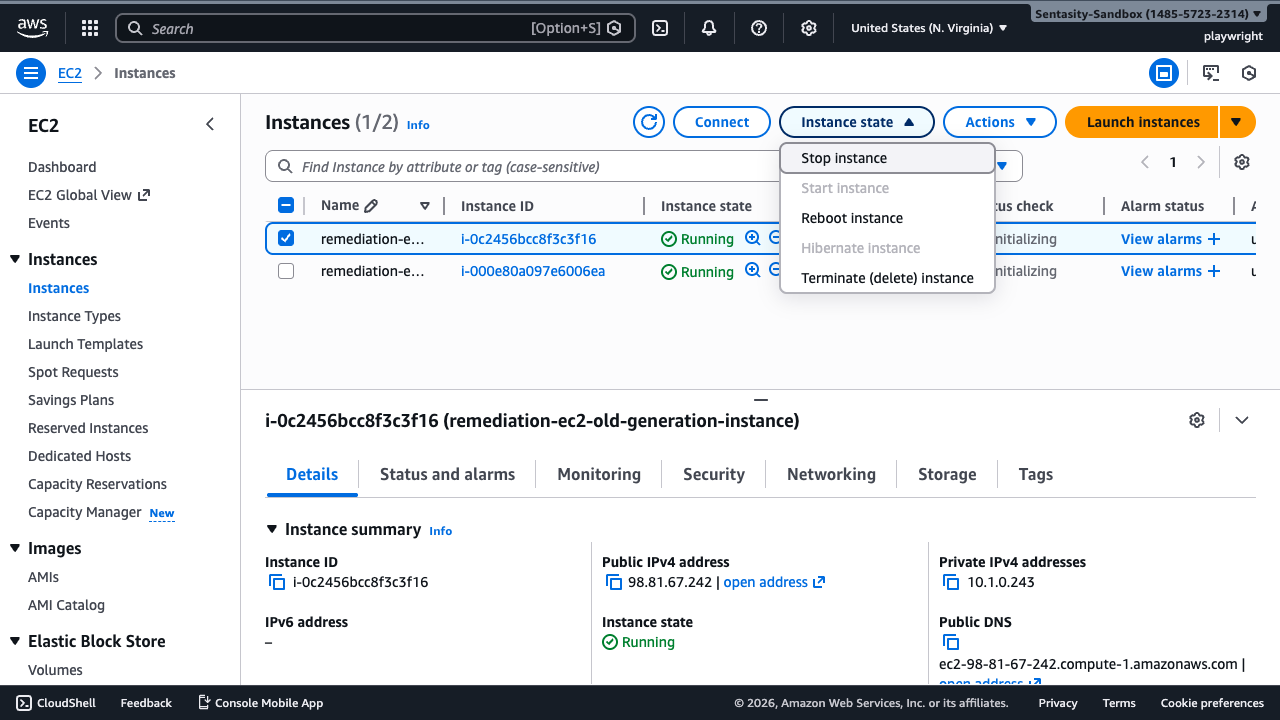
Step 3: Stop the Instance
Before changing the instance type, you must stop the instance:
- Click Instance state → Stop instance
- Confirm the stop action by clicking Stop in the dialog
Note: The instance will be briefly unavailable during this operation, typically taking 30-60 seconds to stop completely.
Step 4: Wait for Instance to Stop
Wait for the instance state to change to Stopped. You can refresh the page to check the current state.
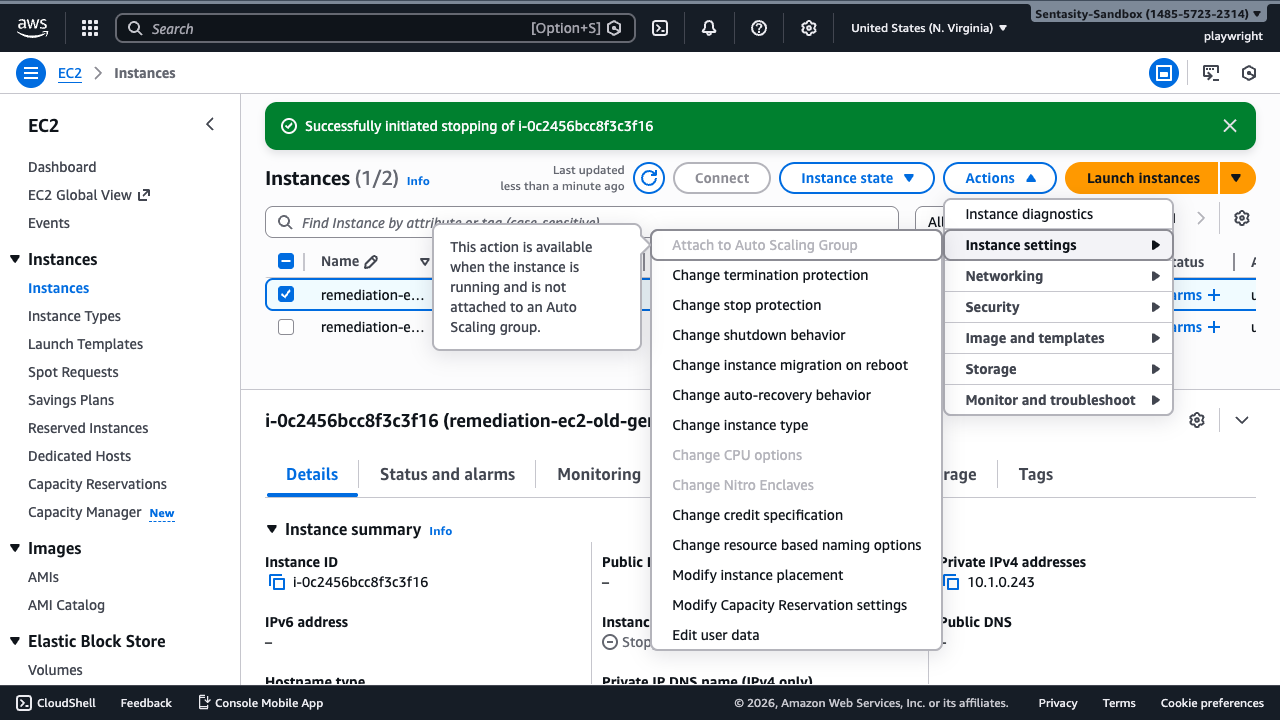
Step 5: Change Instance Type
With the stopped instance selected:
- Click Actions → Instance settings → Change instance type
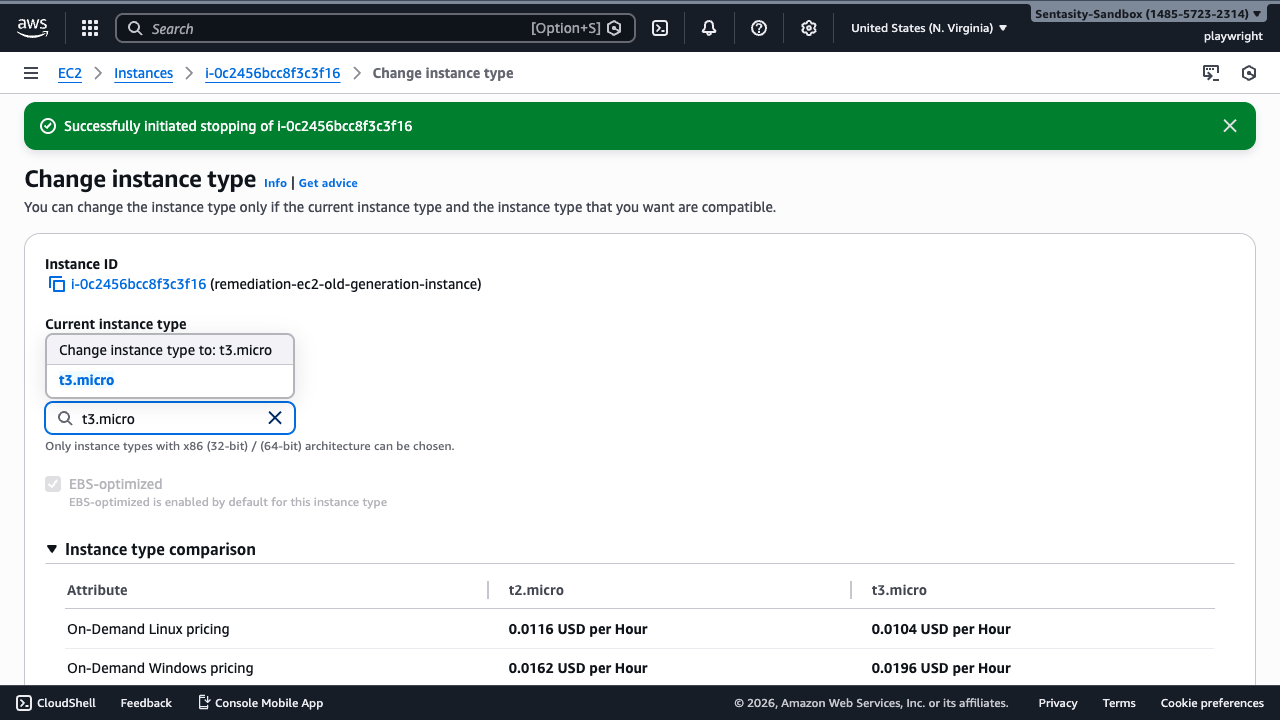
Step 6: Select the New Instance Type
In the "Change instance type" dialog:
- Click the New instance type dropdown
- Type or select t3.micro
- Review the comparison table showing:
- On-Demand Linux pricing: t2.micro ($0.0116/hour) vs t3.micro ($0.0104/hour)
- vCPUs: t2.micro (1 vCPU) vs t3.micro (2 vCPUs)
- Network performance: t2.micro (Low to Moderate) vs t3.micro (Up to 5 Gigabit)
- Click Apply to save the instance type change
Step 7: Start the Instance
Return to the instances list and start the instance:
- Ensure the instance is selected
- Click Instance state → Start instance
Step 8: Verify the Upgrade
Wait for the instance to reach Running state and verify:
- Instance type shows t3.micro
- Instance is running normally with a public IP address
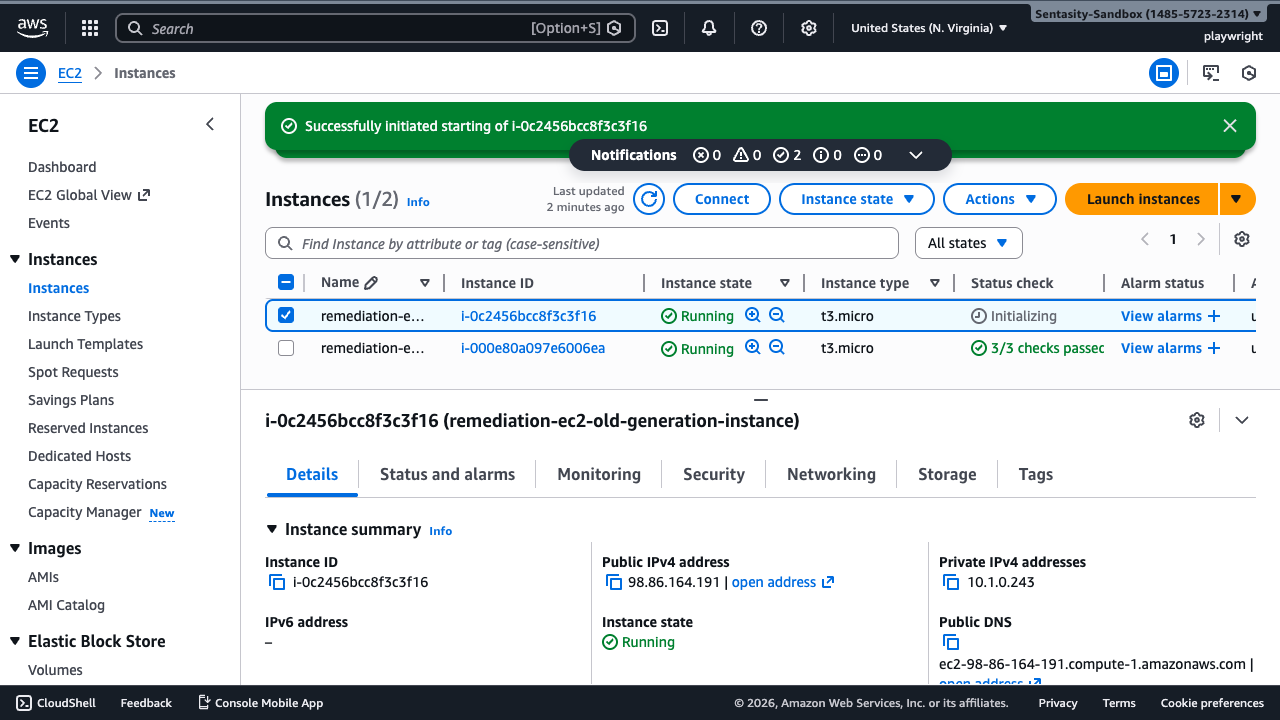
The upgrade is complete! Your instance is now running on the modern t3.micro instance type with improved performance and cost savings.
Alternative Approaches
AWS CLI
You can perform this upgrade programmatically using the AWS CLI:
# Stop the instance
aws ec2 stop-instances --instance-ids i-0c2456bcc8f3c3f16
# Wait for the instance to stop
aws ec2 wait instance-stopped --instance-ids i-0c2456bcc8f3c3f16
# Change instance type
aws ec2 modify-instance-attribute --instance-id i-0c2456bcc8f3c3f16 --instance-type t3.micro
# Start the instance
aws ec2 start-instances --instance-ids i-0c2456bcc8f3c3f16
# Wait for the instance to start
aws ec2 wait instance-running --instance-ids i-0c2456bcc8f3c3f16
Infrastructure as Code
Update your CloudFormation templates or Terraform configurations to use modern instance types:
CloudFormation:
InstanceType: t3.micro # Changed from t2.micro
Terraform:
instance_type = "t3.micro" # Changed from "t2.micro"
Additional Considerations
- Reserved Instances: If you have t2 Reserved Instances, evaluate whether the savings from upgrading outweigh the RI commitment
- t3a alternative: Consider t3a instances for an additional 10% savings if AMD processors are acceptable for your workload
- Graviton instances (t4g): For compatible workloads, t4g instances offer an additional 20% savings beyond t3
- Burstable performance: Both t2 and t3 are burstable instances. Ensure your workload doesn't require sustained CPU performance, or consider non-burstable instance types like m5 or c5
Summary
By upgrading from t2.micro to t3.micro, you've achieved:
- ✅ 10% cost savings (~$0.88/month per instance)
- ✅ Better network performance (up to 5 Gigabit vs Low-Moderate)
- ✅ 2 vCPUs instead of 1 (when burst credits are available)
- ✅ Modern instance generation with better underlying hardware