RDS Stopped Instance
Overview
This guide demonstrates how to handle a stopped RDS database instance. While AWS allows you to stop an RDS instance temporarily to save on compute costs, AWS automatically restarts stopped instances after 7 days. For long-term cost savings, the recommended approach is to create a final snapshot and delete the instance. This eliminates both compute and storage costs while preserving your data for future restoration.
Cost Impact: For a 100GB instance, you eliminate the base storage cost (approximately $9.20/month for gp3) and prevent unexpected compute charges from auto-restart. The snapshot costs approximately the same as storage ($0.095/GB-month) but provides true long-term preservation without auto-restart behavior.
Prerequisites
- AWS Console access with RDS permissions
- An RDS instance in "Stopped" state
Steps
Step 1: Navigate to RDS Console
Navigate to the RDS console to view your database instances.
Step 2: Identify the Stopped Instance
Locate the stopped RDS instance in your databases list. The instance will show a "Stopped" or "Stopping" status.
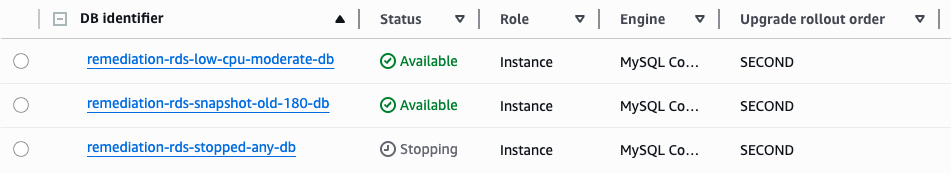
Important: Storage costs continue even while the instance is stopped. AWS will automatically restart this instance after 7 days, which will resume full compute charges.
Step 3: Select and Prepare for Deletion
Select the stopped instance by clicking the radio button next to it. Then click the Actions dropdown and select Delete.
Step 4: Configure Deletion Options
The deletion dialog will appear with several options:
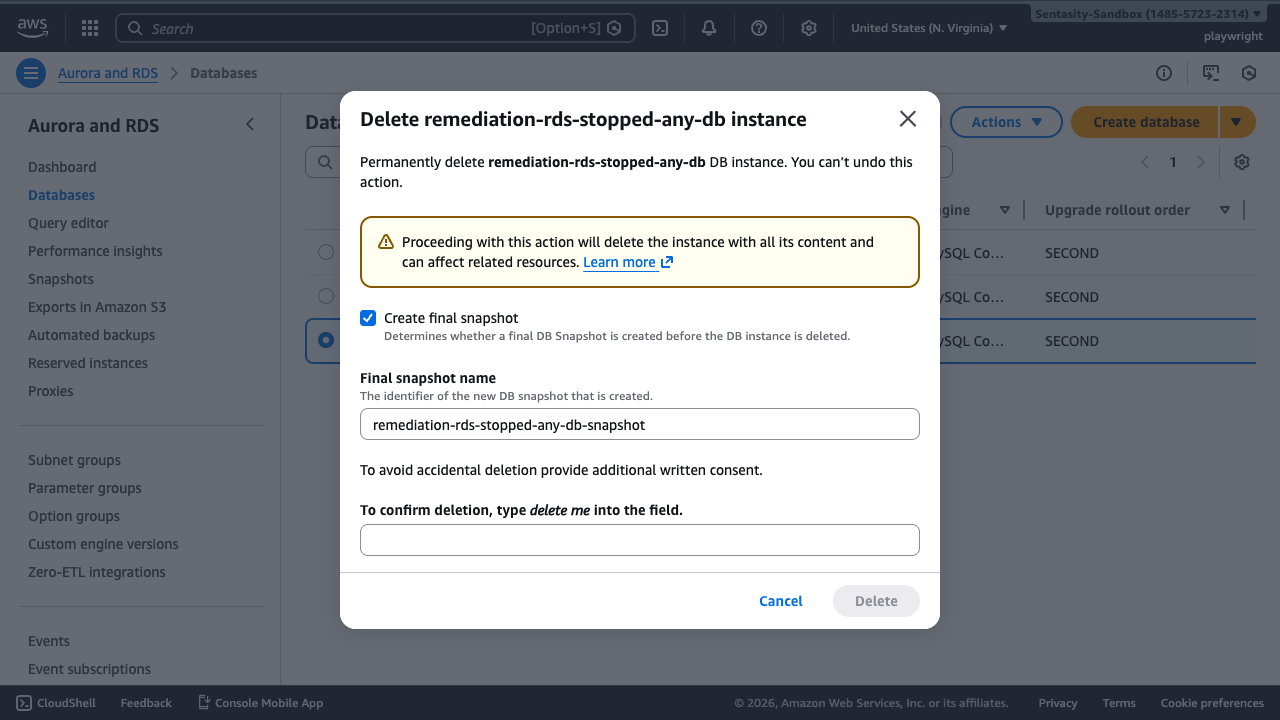
By default, AWS offers to create a final snapshot. You have two choices:
- Create final snapshot (recommended): This preserves your data for future restoration. The snapshot will be created before deletion.
- Skip final snapshot: Only choose this if you're certain you won't need the data.
For this guide, we'll demonstrate the recommended approach of creating a final snapshot.
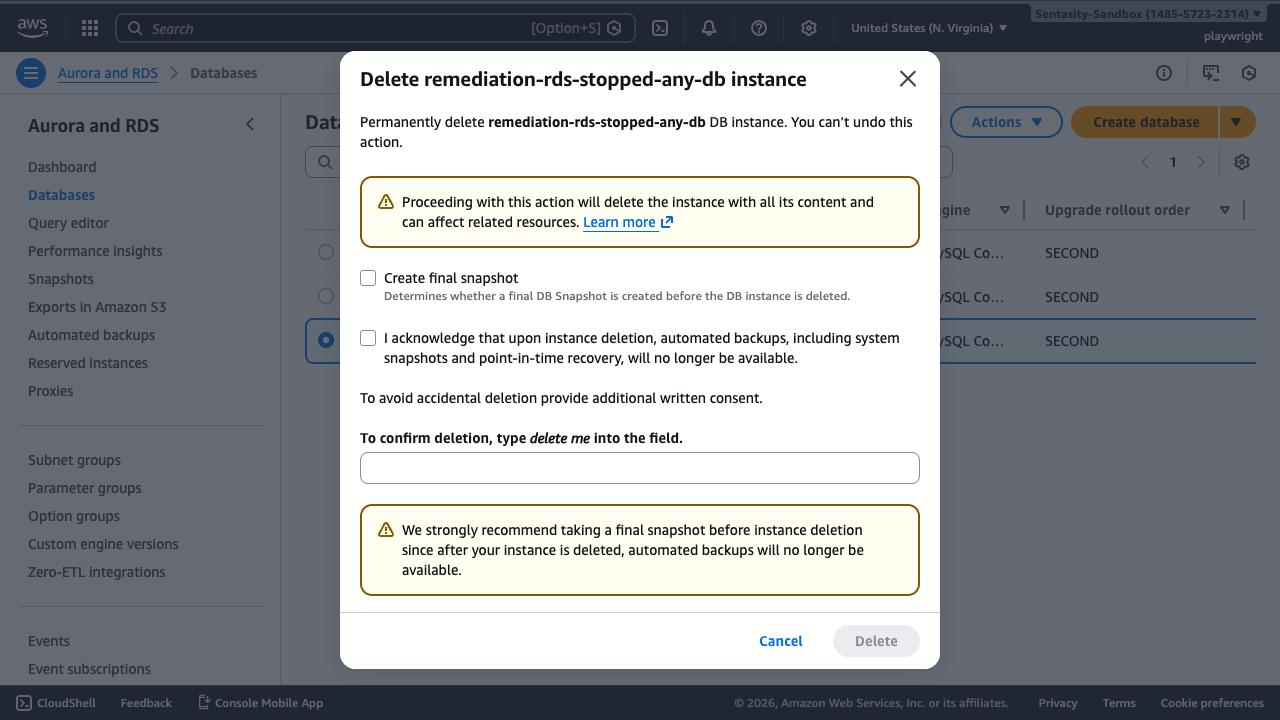
If you uncheck "Create final snapshot", you must acknowledge that automated backups will be deleted. We strongly recommend creating a snapshot before deletion since automated backups won't be available after deletion.
Step 5: Confirm Deletion
To confirm deletion, type delete me in the confirmation field and click Delete.
The instance will be permanently removed along with its ongoing storage costs.
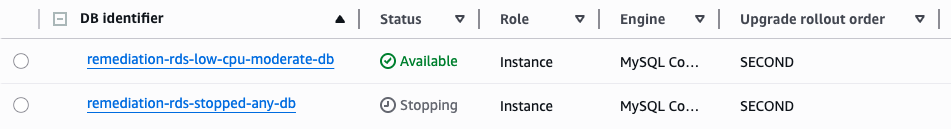
The instance status will show "Deleting" and then disappear from the list once deletion is complete.
Cost Implications
- Eliminated Costs: Base storage costs (~$9.20/month for 100GB gp3) and compute costs
- Prevented Costs: Automatic restart charges after 7 days
- Snapshot Costs: Approximately $0.095/GB-month (similar to storage pricing)
Alternative Approaches
Keep Stopped (Short-term Only)
If you need the instance again within 7 days, you can leave it stopped and restart manually. This works for brief maintenance windows but isn't viable long-term due to the auto-restart limitation.
Scheduled Start/Stop Automation
For dev/test workloads, implement Lambda + EventBridge automation to start instances during business hours and stop them overnight/weekends. This reduces compute costs while accepting the 7-day limitation.
Aurora Serverless v2
For truly variable workloads, consider migrating to Aurora Serverless, which can scale down to minimum capacity (0.5 ACU) automatically. This provides better cost optimization for intermittent usage patterns without manual intervention.
Restoration Process
If you need to restore the instance later:
- Navigate to RDS > Snapshots
- Select your snapshot
- Click Actions > Restore snapshot
- Configure instance settings
- Launch the restored instance (typically takes 5-10 minutes)
Summary
Deleting a stopped RDS instance after creating a snapshot is the most cost-effective approach for long-term storage. You eliminate ongoing storage and prevent unexpected auto-restart charges, while the snapshot provides a restoration path if needed in the future.